From probability to odds to log of odds Everything starts with the concept of probability Let's say that the probability of success of some event is 8 Then the probability of failure is 1 – 8 = 2 The odds of success are defined as the ratio of the probability of success over the probabilityJan 26, 19 · Probability has a limited range from zero to one Odds has an infinite range The probability of something happening is always less than the odds of it happening (assuming the probability is nonzero) The smaller the probability, the more similar probability and odds will beFeb 25, · Odds ratio vs probability ratio Ask Question Asked 1 year, 2 months ago Active 1 month ago Viewed 385 times 8 5 $\begingroup$ An odds is the ratio of the probability of an event to its complement $$\text{odds}(X) = \frac{P(X)}{1P(X)}$$ An odds

Bayes Rule Odds Form Intro Math 1
Is a higher odds ratio better
Is a higher odds ratio better-Dec 08, 18 · Odds seems less intuitive It is the ratio of the probability a thing will happen over the probability it won't In the spades example, the probability of drawing a spade is 025 The probability of not drawing a spade is 1 025Odds as a ratio (eg 43) Results Probability vs Odds Any chance can be numerically described as either odds or probabilities In the majority of circumstances, neither is preferable to the other The majority of scientists generally refer to probabilities, not odds, but that is more a matter of tradition, there is no logical basis for it



Odds Ratio Wikipedia
How to find probability and odds and the difference between the two We also discuss experimental probablility, theoretical probability, odds in favor, andDec 14, 14 · A highly simplified example illustrates this Suppose that 18 out of patients (90 percent probability, odds of 91) in an experiment lost weight while using diet A, while 16 out of (80 percent, odds of 41) lost weight using diet B The relative risk of losing weight by choosing diet A over diet B is 1125, while the odds ratio is about 225Calculating the odds without the number of subjects by the ratio of the number of events (1) by the number of nonevents (4) odds = 1/4 = 025;
Apr 30, · Here, to convert odds ratio to probability in sports handicapping, we would have the following equation (1 / the decimal odds) * 100 or (1 / 25) * 100 Quickly, doing the math in my head (kidding, I used a calculator), the answer is 40% Fractional Odds – How to Convert Odds Ratio to Probability in Sports HandicappingNov 10, 17 · The interpretation of the odds ratio (OR) and prevalence ratio (PR) was assumed as inappropriate when it was interpreted using words as "risk," "(more/less) likely," "probability," or "likelihood" of the event and was assumed as appropriate when it was interpreted as the ratio between odds for the OR or prevalence for the PRAug 18, 19 · When the probability is small (
Many people wrongfully assume odds and probabilities are the same thingThey're definitely not, as there's a significant difference between saying there areOut of 5 times, 1 time will be the event and 4 times will be the nonevent, odds = 025 Odds = 1/5 / 4/5 = 1/4 = 025;The odds ratio for the value of the intercept is the odds of a "success" (in your data, this is the odds of taking the product) when x = 0 (ie zero thoughts) The odds ratio for your coefficient is the increase in odds above this value of the intercept when you add one whole x



Multi Variable Adjusted Odds Ratio For Probability Of Retinopathy Download Table
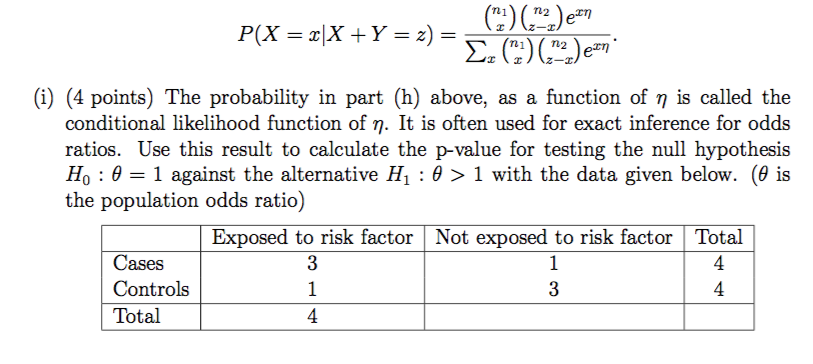


Solved I 4 Points The Probability In Part H Above Chegg Com
Apr 12, 19 · Probability to Odds Probability can be carefully defined using set theory and a few axioms, but the basic idea is that probability uses a real number between zero and one to measure the likelihood of an event occurring There are a variety of ways to think about how to compute this number One way is to think about performing an experiment several timesMar 02, · The odds ratio is the ratio of two odds ODDS RATIO Odds Ratio = Odds of Event A / Odds of Event B For example, we could calculate the odds ratio between picking a red ball and a green ball The probability of picking a red ball is 4/5 = 08 The odds of picking a red ball are (08) / 1(08) = 08 / 02 = 4 The odds ratio for picking a redJul 11, 16 · It's a ratio of events to nonevents You can switch back and forth between probability and odds—both give you the same information, just on different scales If O1 is the odds of event in the Treatment group and O2 is the odds of event in the control group then the odds ratio is O1/O2


Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf



Odds Ratio Wikipedia
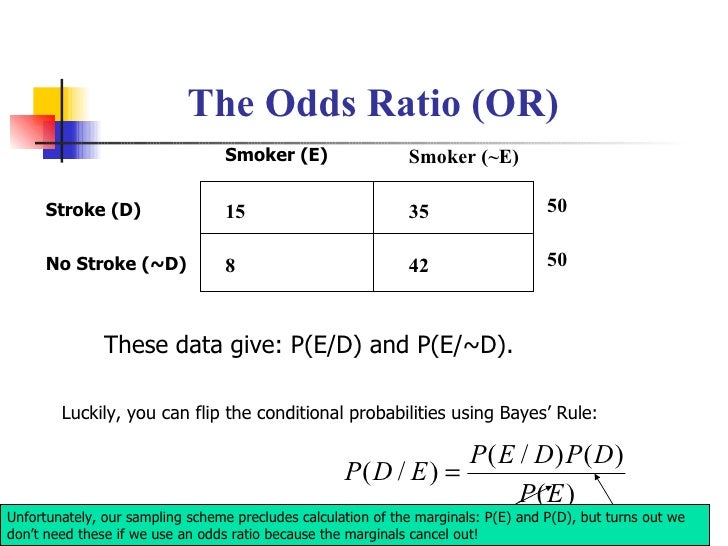
Aug 13, 13 · An odds ratio is a relative measure of effect, which allows the comparison of the intervention group of a study relative to the comparison or placebo group So when researchers calculate an odds ratio they do it like this The numerator is the odds in the intervention arm The denominator is the odds in the control or placebo arm = Odds Ratio (OR)Oct 27, 17 · The probability that an event will occur is the fraction of times you expect to see that event in many trials Probabilities always range between 0 and 1 The odds are defined as the probability that the event will occur divided by the probability that the event will not occur If the probability of an event occurring is Y, then the probability of the event not occurring is 1YThe Odds ratio is 14 x 9,999 Odds ratio = = 14 1 x 9,986 (this is a shortcut formula, only usable in 2x2 tables = n11×n22 n12×n21 where n11 is the upper left, n12 the upper right, etc) almost the same (it is the same if you round it like here) But now a little mathematical fact



Probability Vs Odds Youtube


Log Odds Definition And Worked Statistics Problems
We could use this information to compute an odds ratio O R = / = 544 Thus a female is 544 times more likely to get in But since the probability of an event is just p p q the probability of a male getting in is 30%, while the probability of a female getting in is 70%The point estimate of the oddsratio is 118 and its 95% CI is (, ), based on the CaseControl (Odds Ratio) row below The odds of death penalty are 118 times as high for white defendants as they are for black defendants Recall that a null hypothesis that oddsratio = 1 means that the variables are independentProbability vs Odds ratio Mathematically, probability and odds ratio are two different things Probability is the likelihood that an event will occur, one side of a die out of six possible outcomes Odds ratio is the likelihood that an event will occur in relation to the likelihood that an event will not occur, 1 event for and 5 events against



Bayes Rule Odds Form Intro Math 1


9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science
Definition of Odds The odds of an event occurring is the ratio of the number of ways the event can occur (successes) to the number of ways the event cannot occur (failures)Oct 07, 11 · Definition The Odds Ratio is a measure of association which compares the odds of disease of those exposed to the odds of disease those unexposed Formulae OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in the nonexposed) Example I often think food poisoning is a good scenario to consider when interpretting ORs Imagine a group of friends went out toOct 24, · Odds can be expressed as a ratio of the probability an event will happen divided by the probability an event won't happen Odds in favor of A = A / (1 A), usually simplified to lowest terms, For instance, if the probability of an event occurring is 075, then the odds for it happening are 075/025 = 3/1 = 3 to 1 for, while the probability that it doesn't occur is 1 to 3



Probability Odds Odds Ratio Youtube



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
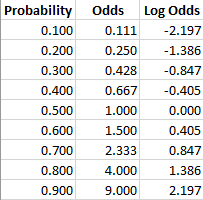
Odds the ratio of the probability that an event will occur versus the probability that the event will not occur, or probability / (1probability) For example, if you are normally on call 2 out of 7 days in a week, then the odds of you being on call on a certain day of the week is (2/7)/(5/7) = 040E) But what about the Odds ratio?Feb 03, 14 · Converting between odds and probability Converting Odds to Probability Simply add the 2 components of the odds together to make a new denominator, and use the old numerator eg If the odds are 35, or 3 to 5, the probability is 3 ÷ (35) = 3/8 = 375% Converting Probability to Odds Take the probability, and divide it by its compliment



Odds Ratio Sage Research Methods



How To Place Odds Ratio Of Y Value At One Standard Deviation Above And Below Mean Of X To A Ggplot Or Other R Plot Stack Overflow
Pretest probability and posttest probability (alternatively spelled pretest and posttest probability) are the probabilities of the presence of a condition (such as a disease) before and after a diagnostic test, respectively Posttest probability, in turn, can be positive or negative, depending on whether the test falls out as a positive test or a negative test, respectivelyDec 07, · Fractional odds are sometimes called British odds or traditional odds and are sometimes written as a fraction, such as 6/1, or expressed as a ratio, like sixtoone Decimal odds represents theJun 02, 09 · Probability = 1/5 = 02;



Solved Select All Of The True Statements Regarding The Od Chegg Com



Odds Ratio Forecasts Increase Precautionary Action For Extreme Weather Events In Weather Climate And Society Volume 4 Issue 4 12
When playing a lottery or other games of chance be sure you understand the odds or probability that is reported by the game organizer A 1 in 500 chance of winning, or probability of winning, is entered into this calculator as "1 to 500 Odds are for winning" You may also see odds reported simply as chance of winning as 5001The odds of winning are 1/9,999 () and the probability of winning is 1/10,000 () In this case, odds and probability are essentially identical Relative Risk (RR) & Odds Ratio (OR) The difference between odds and probability is important because Relative Risk is calculated with probability and Odds Ratio is calculated with odds2 Make a rough estimate of the post test probability 3 Use a likelihood ratio calculator 4 Use a nomogram 11 Get a qualitative sense A relatively high likelihood ratio of 10 or greater will result in a large and significant increase in the probability of a disease, given a positive test



Odds Ratio Wikiwand


Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression
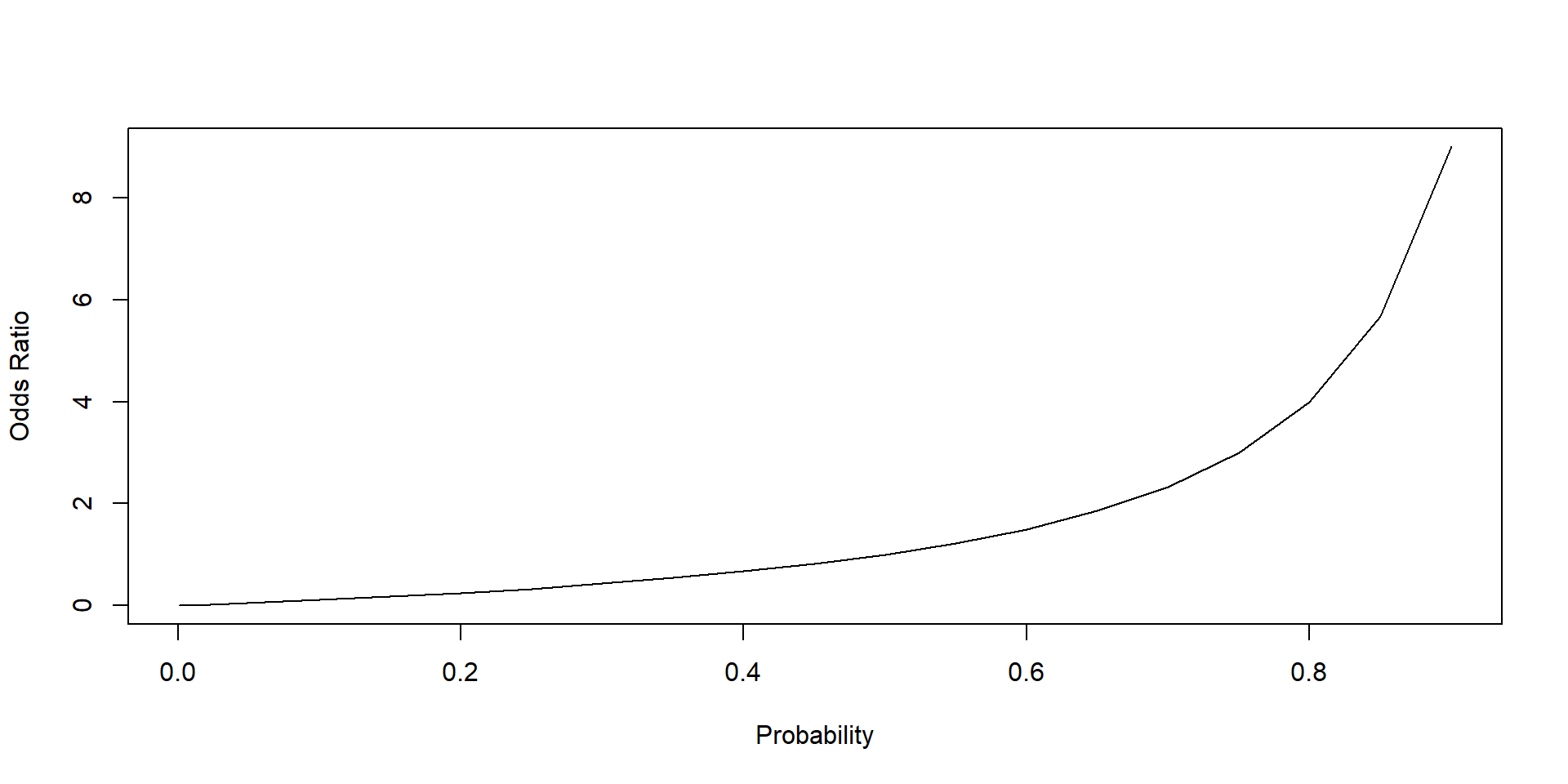
The magnitude of the odds ratio is called the "strength of the association" The further away an odds ratio is from 10, the more likely it is that the relationship between the exposure and the disease is causal For example, an odds ratio of 12 is above 10, but is not a strong association An odds ratio of 10 suggests a stronger associationOct , 18 · Summary Our theoretical Odds Ratio is 0319 with a CI(0, 041), which is close to the true Odds ratio, 03This indicates if the undergraduate students are from the school in prestige 3 or 4, the chances of them getting in graduate school is 38% that of the students from prestige 1 or 2 undergraduate schoolsJun 01, 12 · Odds ratios work the same An odds ratio of 108 will give you an 8% increase in the odds at any value of X Likewise, the difference in the probability (or the odds) depends on the value of X So if you do decide to report the increase in probability at different values of X, you'll have to do it at low, medium, and high values of X



Logit Wikipedia
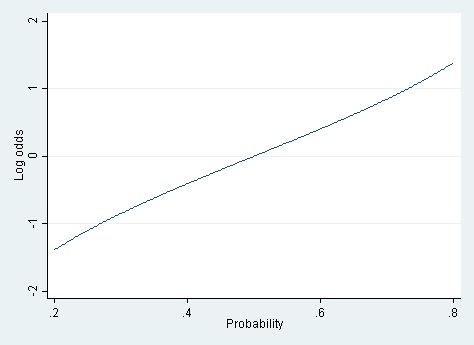


Linear Vs Logistic Probability Models Which Is Better And When Statistical Horizons
Posttest probability for negative test = c / (cd) = 30 / 1 = 25% = 025 So, as we expect from the likelihood ratios for this test, given a "starting point" of 50% for the overall prevalenceAs an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 10 (1% = 01% x 10), more than 10 times higherFeb 19, 18 · While odds are expressed in the ratio, the probability is either written in percentage form or decimal Odds usually ranges from zero to infinity, wherein zero defines impossibility of occurrence of an event, and infinity denotes the possibility of occurrence Conversely, probability lies between zero to one



Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Numbers Of Women With Events With Odds Ratios And Probability Of Download Table
Pretest odds × Likelihood ratio = Posttest odds To use this formulation, probabilities must be converted to odds, where the odds of having a disease are expressed as the chance of having the disease divided by the chance of not having the disease For instance, a probability of 075 is the same as 31 odds (Figure 1–8)Calculating Probability Given Odds To calculateThus, when the probability of X occurring in group B is greater than the probability of X occurring in group A, the odds ratio is greater than 1, and the log odds ratio is greater than 0 Suppose that in a sample of 100 men, 90 drank wine in the previous week, while in a sample of 80 women only drank wine in the same period



Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Odds Ratio (OR) measures the association between an outcome and a treatment/exposure Or in other words, a comparison of an outcome given two different groups (exposure vs absence of exposure) OR is a comparison of two odds the odds of an outcome occurring given a treatment compared to the odds of the outcome occurring without the treatmentAug 26, · Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while a 12 paperMar 23, 09 · A probability of 0 is the same as odds of 0 Probabilities between 0 and 05 equal odds less than 10 A probability of 05 is the same as odds of 10 Think of it this way The probability of flipping a coin to heads is 50%


Logistic Regression Reporting Odds Ratios Youtube



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
Jul 31, 11 · Probability vs Odds Real life is full of incidents with uncertainty The terms probability and odds measure one's belief in the occurrence of a future event It may confuse since both 'Odds' and 'probability' are related to the potential that event occurs However, there is a difference Probability is a broader mathematical conceptInterpreting Odds Ratios An important property of odds ratios is that they are constant It does not matter what values the other independent variables take on For instance, say you estimate the following logistic regression model 1685 x 1 0039 x 2 The effect of the odds of a 1unit increase in x 1 is exp(1685) = 118


Probability Vs Odds What S The Difference Learn It And By Z Ai Towards Data Science



Comparing A Relative Risk To An Odds Ratio Academic Website Of Dr Einar Holsbo



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal
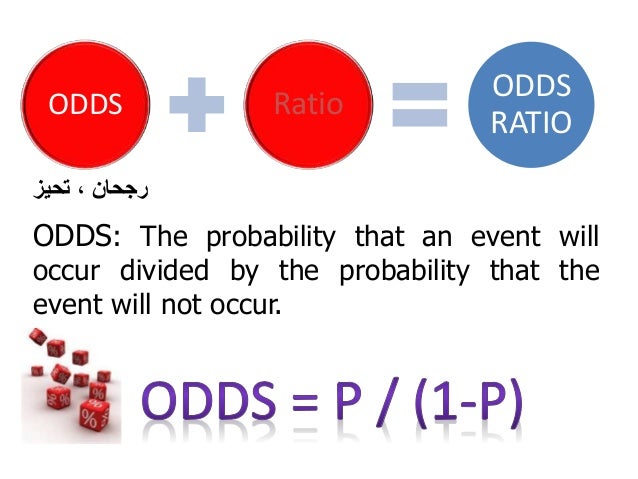


Odds Ratios Basic Concepts



Sw318 Social Work Statistics Slide 1 Logistic Regression And Odds Ratios Example Of Odds Ratio Using Relationship Between Death Penalty And Race Ppt Download



Statistics 12 Probability Vs Odds Stats Seandolinar Com


Odds Ratio For A Simple Distribution Jmp User Community



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Odds Ratio Analysis For The Groups Defined By Predicted Pd Probability Download Table



The Difference Between The Logits Of Two Probabilities Is The Logarithm Of The Odds Ratio Correct Incorrect Cross Validated



Relative Risk Wikipedia



How To Calculate Odds 11 Steps With Pictures Wikihow



Lecture3


Odds Likelihood Ratios Guide To Diagnostic Tests


Odds Vs Probability Vs Chance Data Science Central



Pdf How Much More Likely The Implications Of Odds Ratios For Probabilities Semantic Scholar


Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsterm



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
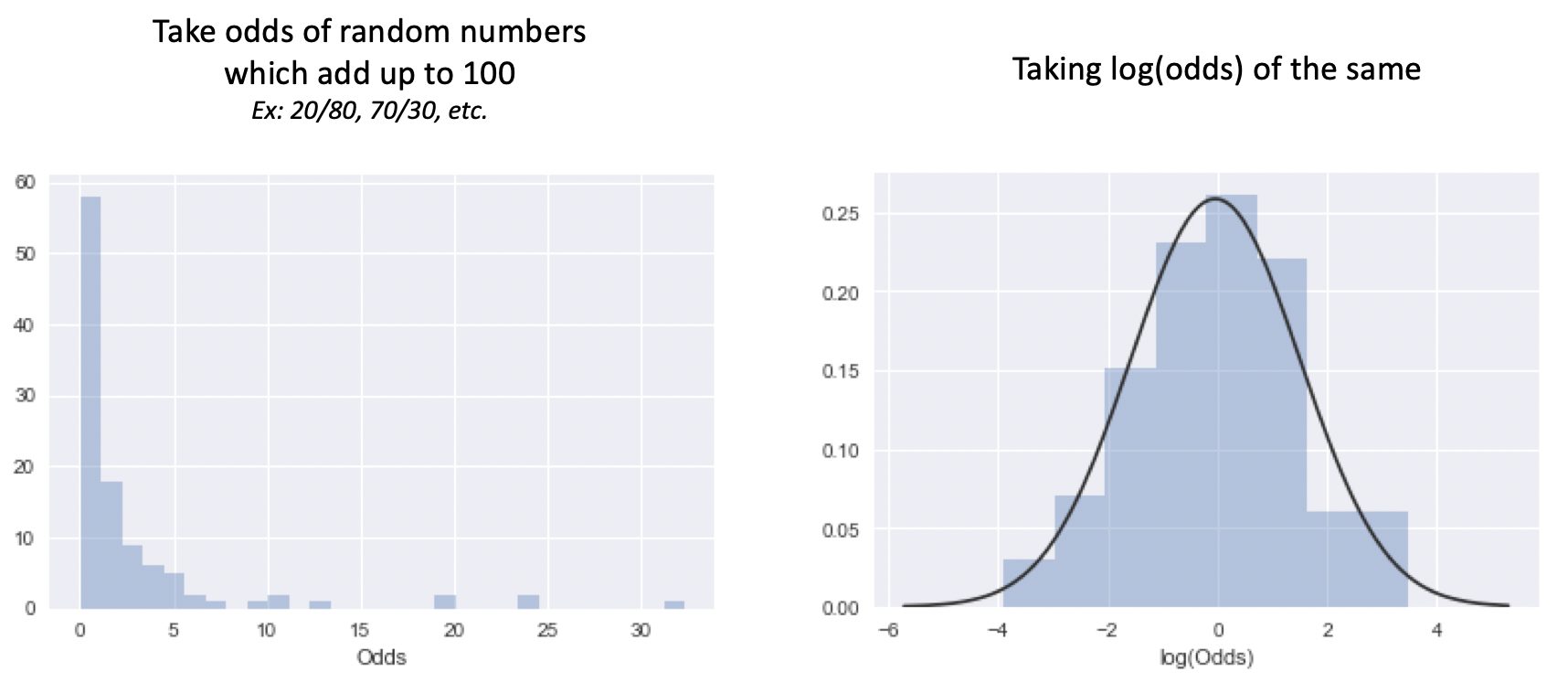


What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science


Are You Mixing Up Odds With Probability By Keith Mcnulty Towards Data Science



Ppt Conditional Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube



Nhanes Tutorials Module 10 Logistic Regression



Pro X Odds Ratio And Conditional Probabilities Download Table


Lecture3



Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube


Logit Model



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science


Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research



Logistic Regression Estimates Odds Ratios Of The Probability Of Download Table



Facing Page Probability Of Survival And Odds Ratios For Death Download Scientific Diagram
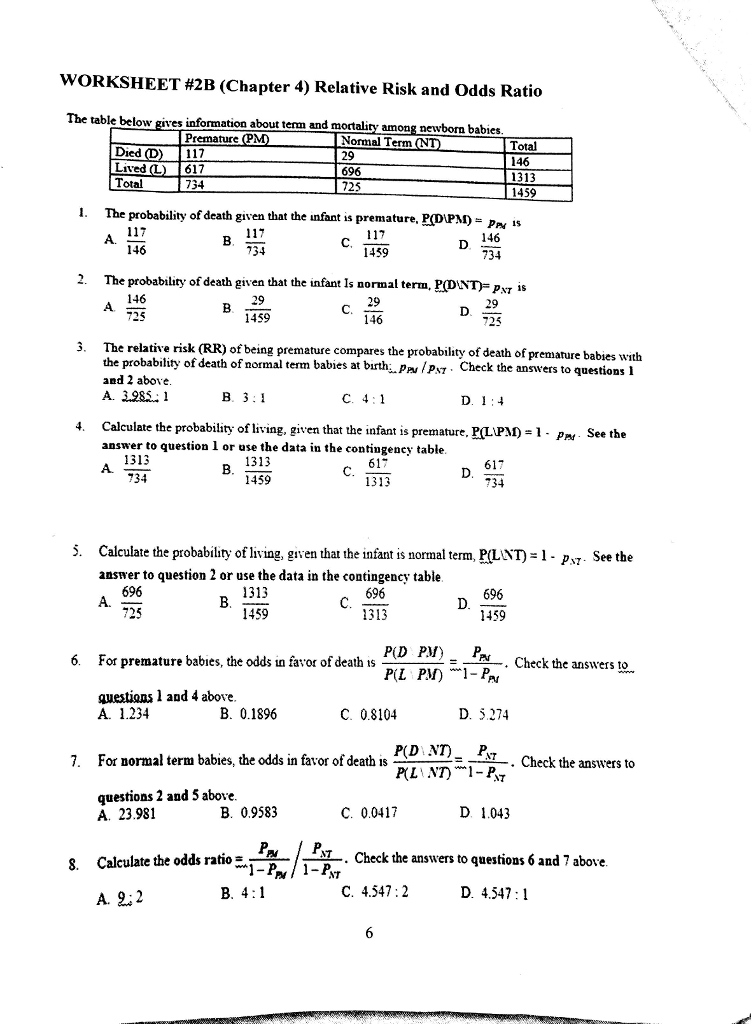


Solved The Table Below Gives Information About Term And M Chegg Com



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
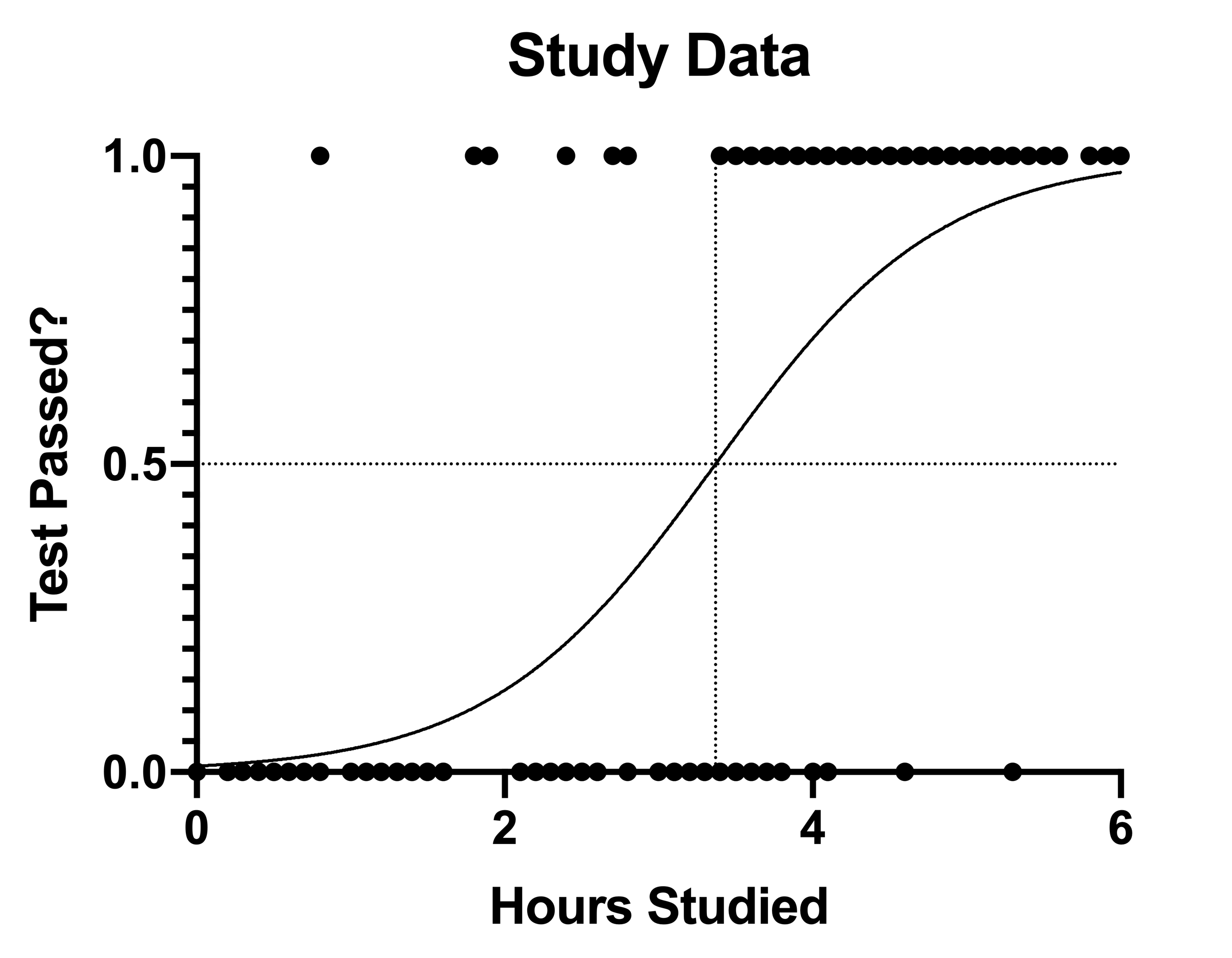


Graphpad Prism 9 Curve Fitting Guide Example Simple Logistic Regression



Webinar Recording Signup
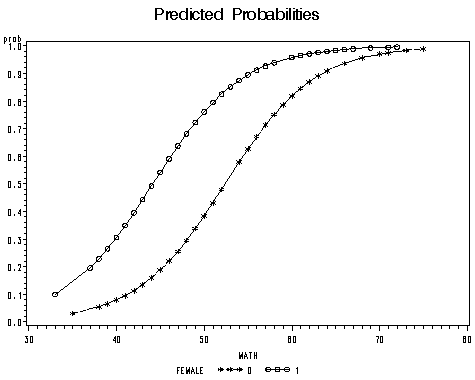


Proc Logistic And Logistic Regression Models
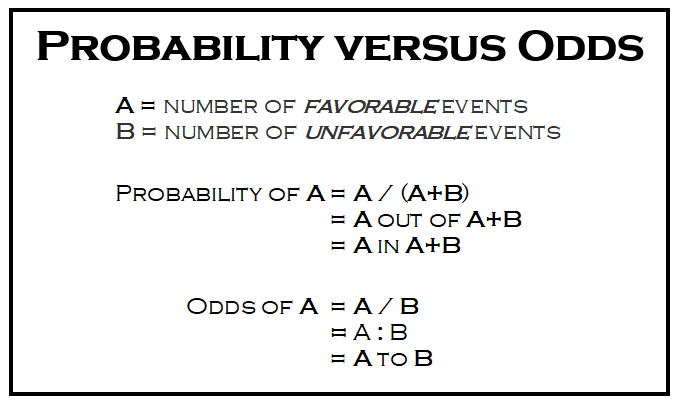


What Are The Odds Stats With Cats Blog



1 A Comparison Of Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio With The Average Marginal Download Scientific Diagram



Bayes Theorem Is Used To Calculate The Probability Of An Outcome



How To Calculate Odds Ratios And Probabilities In Case Control Studies Cross Validated
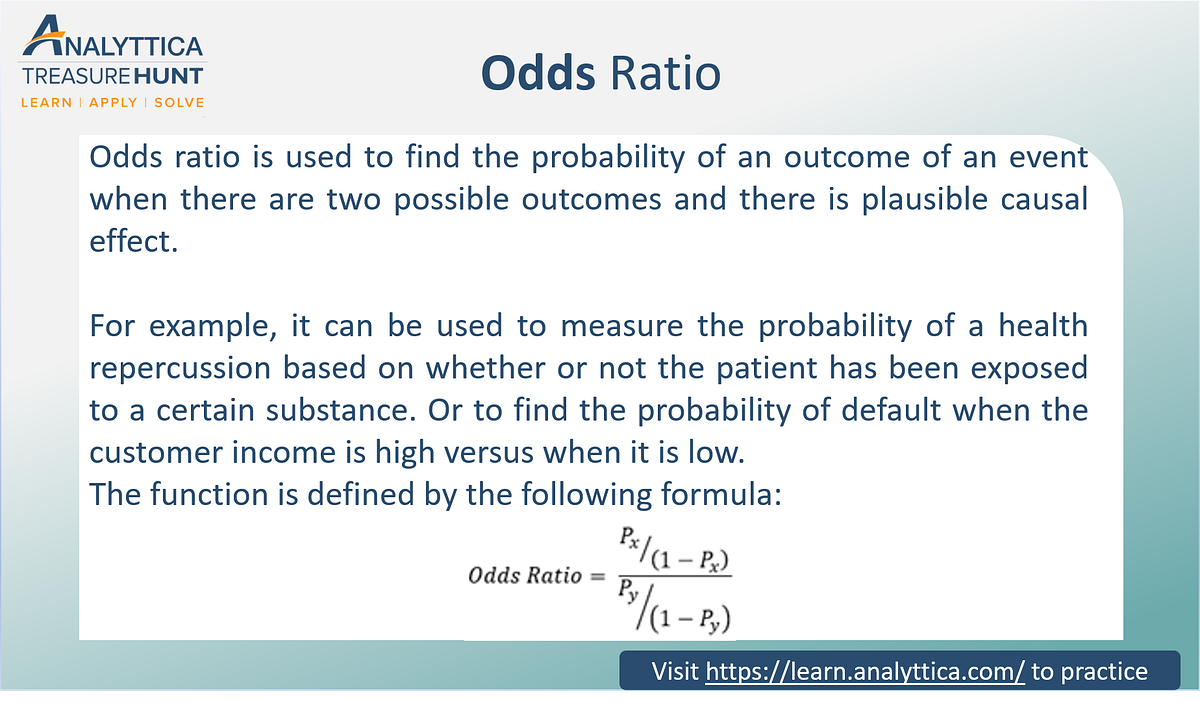


Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium



Are You Mixing Up Odds With Probability By Keith Mcnulty Towards Data Science


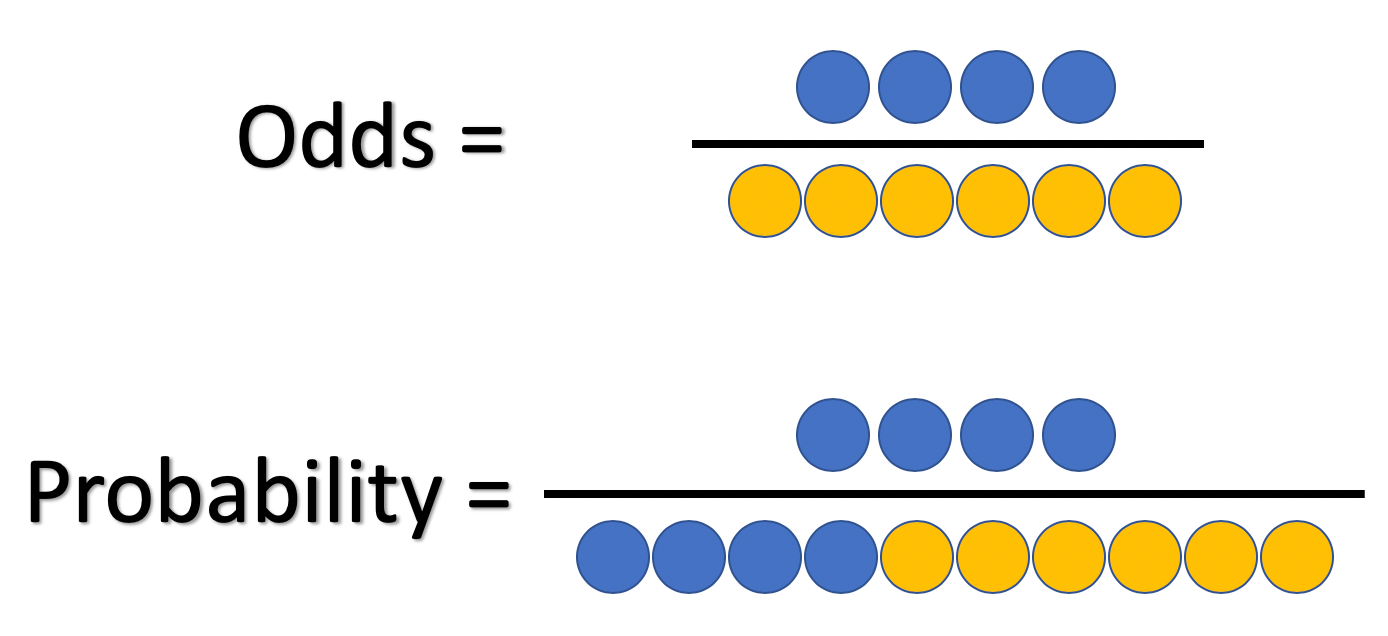
The Difference Between Probability And Odds


What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science



Lecture3
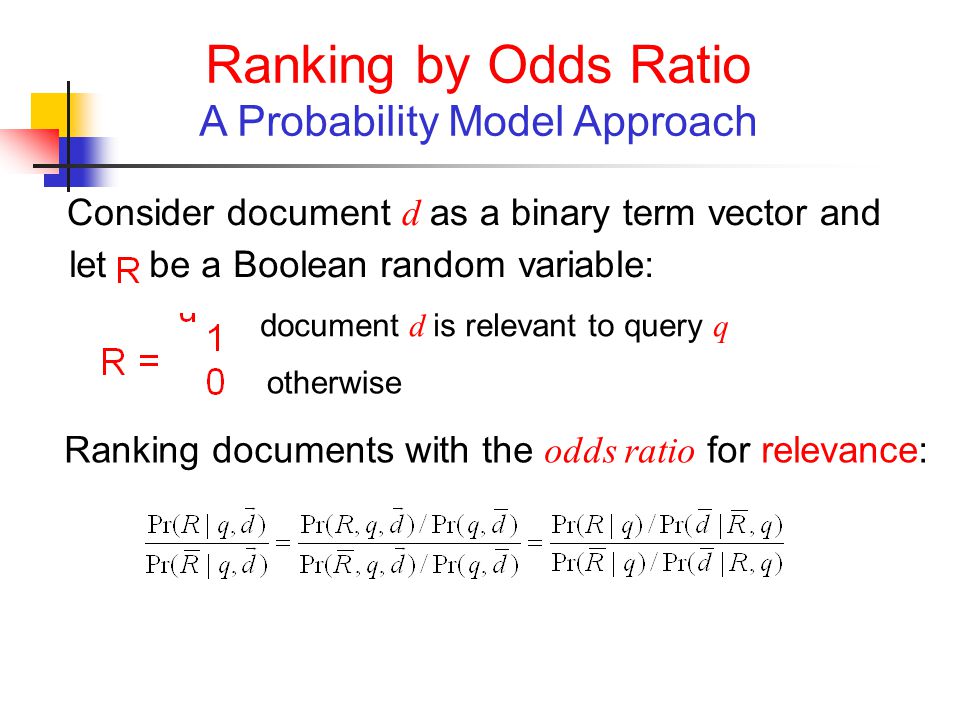


Ranking By Odds Ratio A Probability Model Approach Let Be A Boolean Random Variable Document D Is Relevant To Query Q Otherwise Consider Document D As Ppt Download



Example 8 29 Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios R Bloggers



Probability Vs Odds What S The Difference Learn It And By Z Ai Towards Data Science


Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



R Calculate And Interpret Odds Ratio In Logistic Regression Stack Overflow



What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science
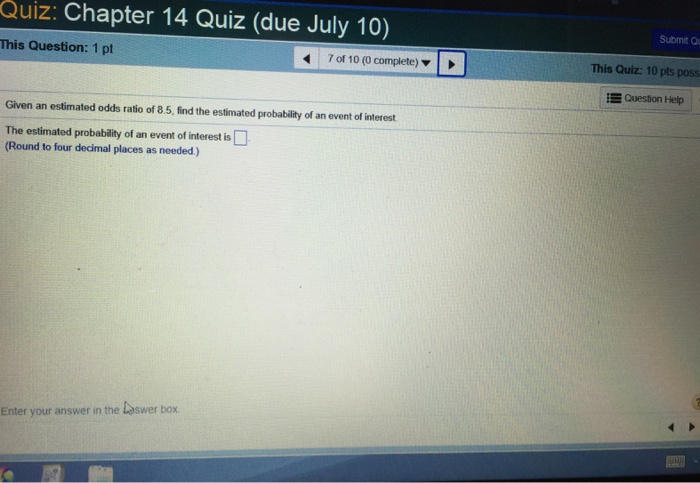


Solved Given An Estimated Odds Ratio Of 8 5 Find The Est Chegg Com



Measuring Association Using Odds Ratios R Bloggers
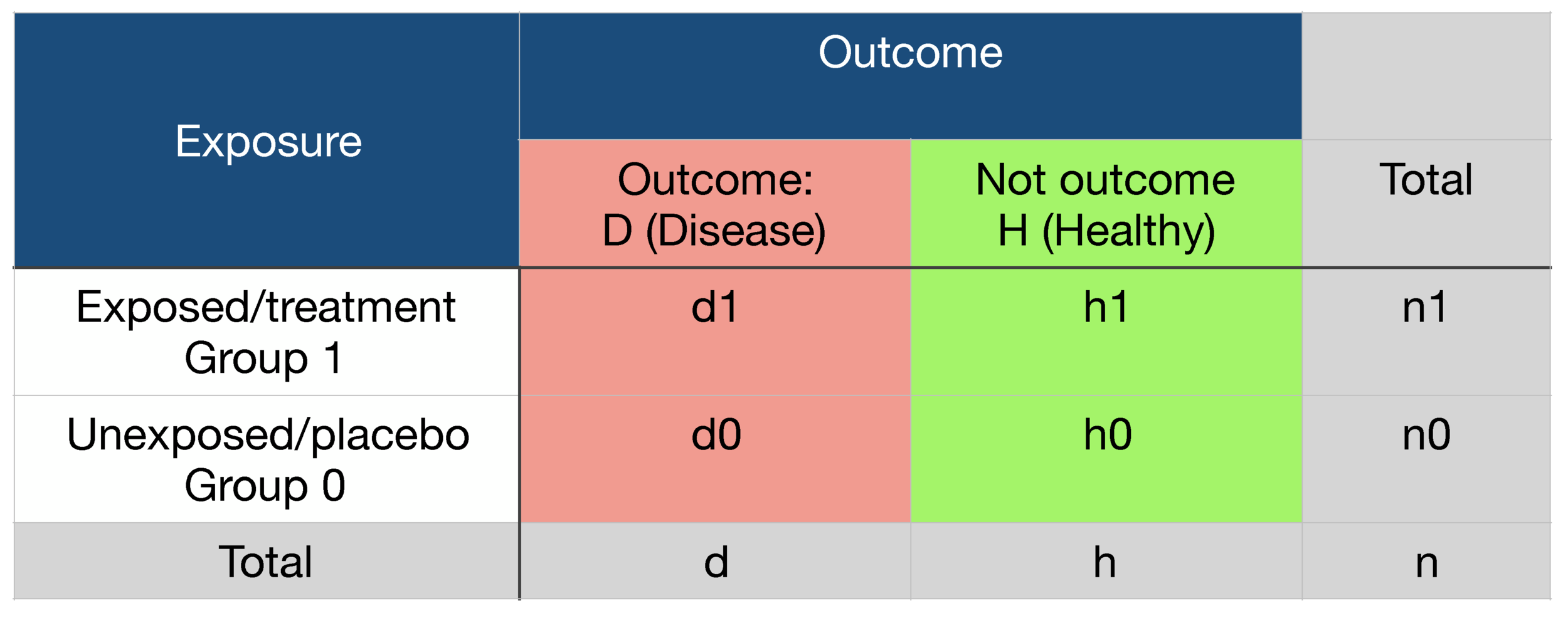


Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gp Raj



Converting Between Probability And Odds Mathwoes Youtube
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_The_Math_Behind_Betting_Odds_and_Gambling_Nov_2020-01-735accb453c8424b9e063c2c14e4edf4.jpg)


The Math Behind Betting Odds Gambling



Solved Question 4 1 Pts Where P Is The Odds Ratio Is Defi Chegg Com



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal


Odds Likelihood Ratios Guide To Diagnostic Tests



Binary Logistic Regression With Odds Ratios Calculated For The Download Table



Logit Of Logistic Regression Understanding The Fundamentals By Saptashwa Bhattacharyya Towards Data Science



Relationship Between Rr And Or A Rr Probability A Probability B Download Scientific Diagram



How To Interpret Odds Ratios Statology



Odds Ratios And Marginal Probability By Small Medium And Large Effect Download Scientific Diagram



Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To



Odds Ratio Sage Research Methods
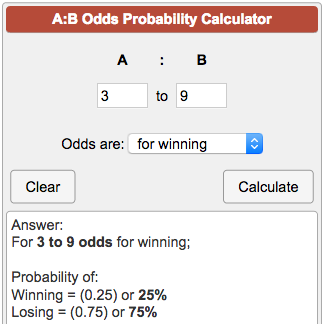


Odds Probability Calculator



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube
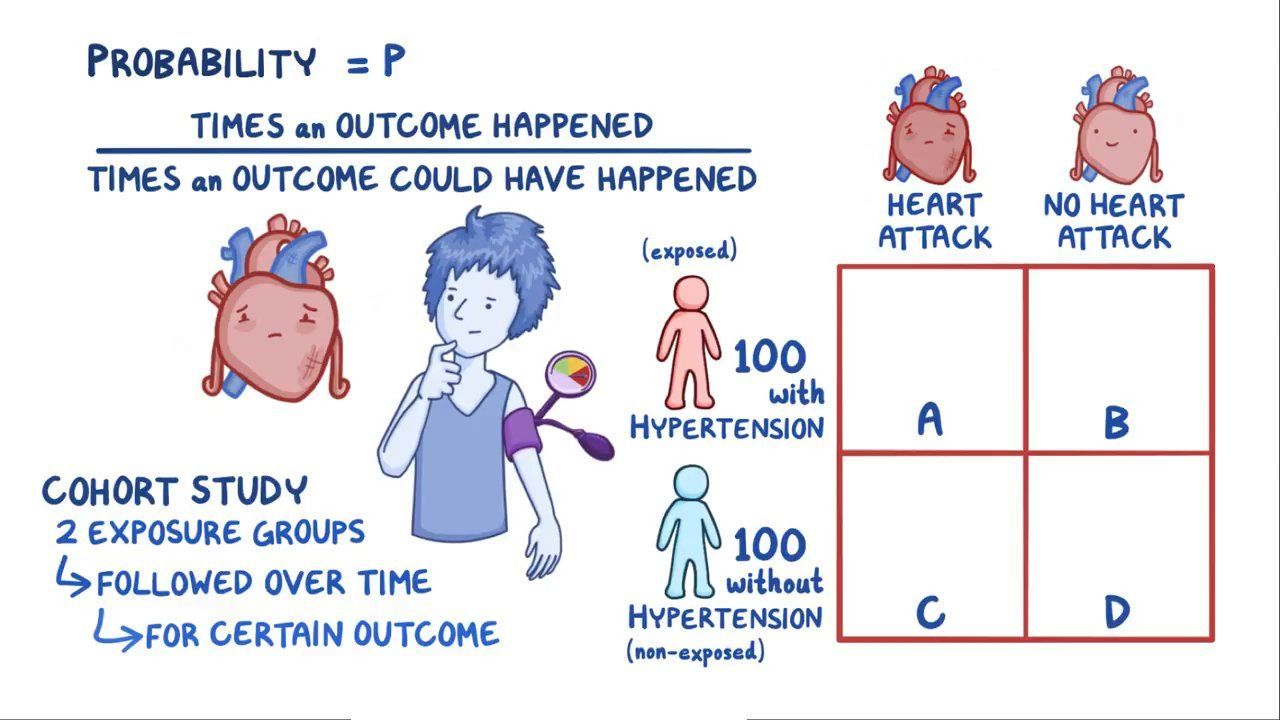


Odds Ratio Osmosis



Odds Vs Probabilities Odds Ratio In Spss Exp B Is An Odds Rather Than A Probability Odds Success Failure Probability Likelihood Of Success For Ppt Download



Pdf How Much More Likely The Implications Of Odds Ratios For Probabilities Semantic Scholar



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



Estimated Z Score Odds Ratio And The Corresponding Probability For The Download Table



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿